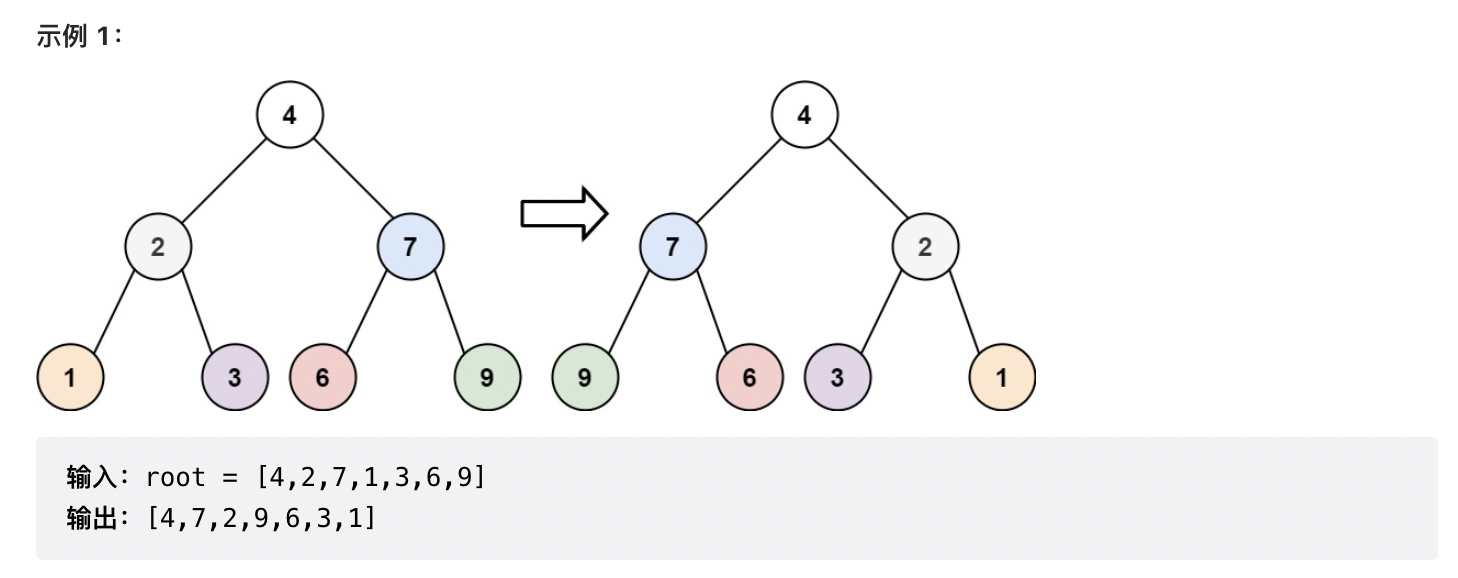
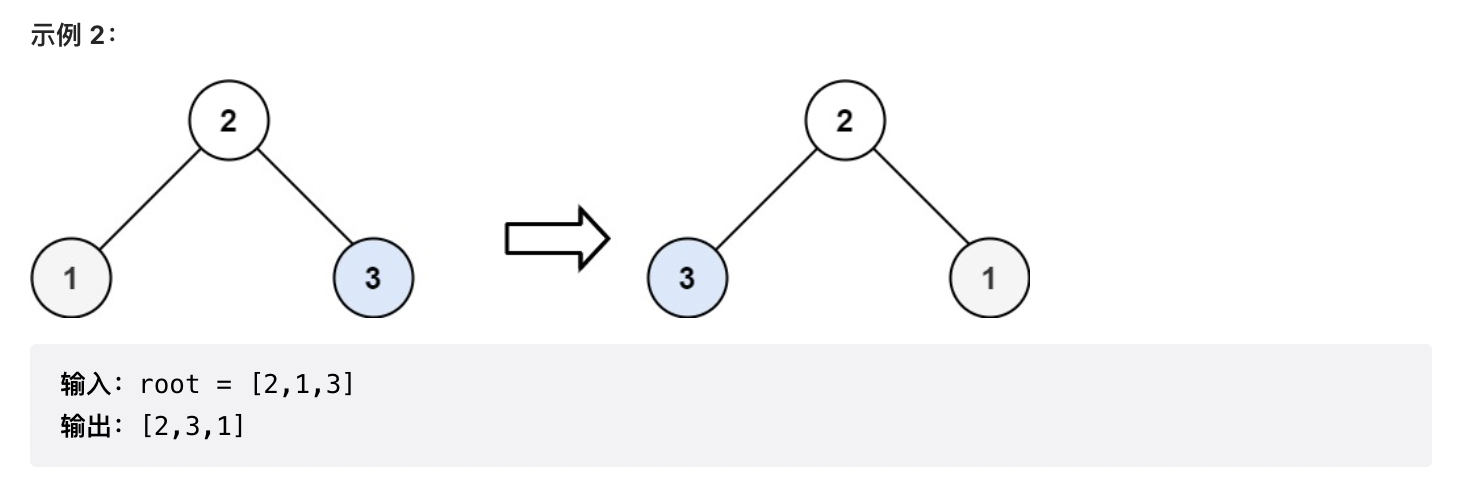
给你一棵二叉树的根节点root,翻转这棵二叉树,并返回其根节点
一、递归
步骤如下:
- 翻转根节点的左子树(递归调用当前函数)
- 翻转根节点的右子树(递归调用当前函数)
- 交换根节点的左子节点与右子节点
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode(int x) { val = x; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public TreeNode invertTree (TreeNode root) {
if (root == null)
return null;
invertTree(root.left);//翻转根结点的左子树
invertTree(root.right);//翻转根结点的右子树
TreeNode tmp = root.left; //交换左子节点和右子节点
root.left = root.right;
root.right = tmp;
return root;
}
}
二、迭代法-队列
迭代法的思路是BFS或者DFS,实际上也是二叉树的遍历。BFS用Queue实现,DFS的话将代码中的Queue换成Stack
这是一种非递归层次遍历,借助于队列,元素先进先出。时间复杂度 O(N) 空间复杂度 O(1)
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode(int x) { val = x; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public TreeNode invertTree(TreeNode root) {
//LinkedList实现了集合框架的Queue接口
Queue<TreeNode> q = new LinkedList<TreeNode>();
if(root!=null) q.offer(root);//加入元素
while(!q.isEmpty()){
TreeNode curr = q.poll();//获取并移出元素
TreeNode tmp = curr.right;
curr.right = curr.left;
curr.left = tmp;
if(curr.left!=null) q.offer(curr.left);
if(curr.right!=null) q.offer(curr.right);
}
return root;
}
}
三、迭代法-栈
和队列不同,这是先进后出的方式
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode(int x) { val = x; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public TreeNode invertTree(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null) {
return null;
}
Stack<TreeNode> stack = new Stack<>();
stack.push(root);//先将根节点压入堆栈
while (stack.size() > 0) {
//根据栈的先进后出操作,获取栈中最后一个元素,即最先入栈的元素
TreeNode temp = stack.lastElement();
stack.pop();//弹出栈顶元素
//交换左右子树
TreeNode tempLeft = temp.left;
temp.left = temp.right;
temp.right = tempLeft;
//左子树不为空,将左子树入栈
if (temp.left != null) {
stack.push(temp.left);
}
//右子树不为空,将右子树入栈
if (temp.right != null) {
stack.push(temp.right);
}
}
return root;
}
}

评论